
![]()
Product Introduction
A cold rolled steel sheet is produced by pickling a hot coil and rolling it uniformly at an appropriated temperature to a thinner thickness. It has excellent surface configuration and superb mechanical properties for use in automobile and electronic appliance production.
Manufacturing availability
Quality Specifications
|
Classification |
KSD 3512 | JIS G3141 | ASTM A1008 | EN10130 |
|
CQ (Commercial Quality) |
SPCC | SPCC | CS |
DC01(Fe P01) |
|
DQ (Drawing Quality) |
SPCD | SPCD | DS |
DC03(Fe P03) |
|
DDQ (Deep Drawing Quality) |
SPCE | SPCE | DDS |
DC04(Fe P04) |
|
DDQ-N (StabilizedDeep Drawing Quality) |
SPCEN | SPCEN | DDS |
DC04(Fe P04) |
|
EDDQ |
EDDS |
DC05(Fe P05) |
Classification of Products
- Commercial / Sheet of this quality is for simple bending or moderate forming. Commercial steel sheet can be bent flat upon itself in any direction at room temperature. It has a wide variety of uses, including automotive panels, electrical home appliances, drums, pipes, farm implements, office supplies, building and civil work materials, and as base metal for various coatings.
- Drawing / Sheet of this quality has a greater degree of ductility and is more consistent in performance than commercial steel because of higher standards in production, selection and melting of the steel. It is suitable for automotive panels, audio-visual equipment, and heating apparatuses.
- Deep Drawing / Sheet of this designation should be used when drawing steel will not provide a sufficient degree of ductility for fabrication of parts with stringent drawing requirements, or applications that require the sheet be free from aging. This quality is produced through special steelmaking and finishing practices. It is suitable for automotive front panels and rear fenders.
- Stabilized Deep Drawing / Stabilized deep drawing quality products boast the highest quality in terms of workability. It is suitable for automotive parts that require complicated treatment such as front fenders or wire. As a non-aging deep drawing sheet made with Al-killed, quality is guaranteed against extreme stretching or straining.
- Surface Finish / The surface finish of cold-rolled steel sheet is either dull or bright.
- Dull Finish / Dull finish, which is attained by attaching numerous fine grains onto the steel surface, is often called 'pear-skin finish' or 'egg-shell texture'. The grains are made by steel grit blasted roll. The dull finish is useful in drawing because lubricant oil can be evenly spread over the entire surface, thereby reducing the possibility of friction. The fine grains also help boost paint adherence and extend the steel life span of the steel.
- Bright Finish / Bright finish presents high-quality roughness that is optimal for decorative purposes. The sheet surface is rolled with fine polished rolls.
Edges
|
Classification |
Specifications |
| Mill Edge | Edges produced by trimming hot rolled coil during the pickling process, prior to cold rolling. |
| Slit Edge (Trimmed Edge) |
Edges produced by shearing or slitting during the cold rolling process. |
Oiling
Sheet that is processed with the final step being the application of oil to the surface; usually intended to provide protection from rusting during shipment and storage. The oil may also serve to assist in the subsequent fabrication process, but this is not usually the main purpose. Dongbu Steel delivers its steel products either oiled (heavy, general or light, dos oiling, powdering) or un-oiled.
Testing Methods
Testing Methods
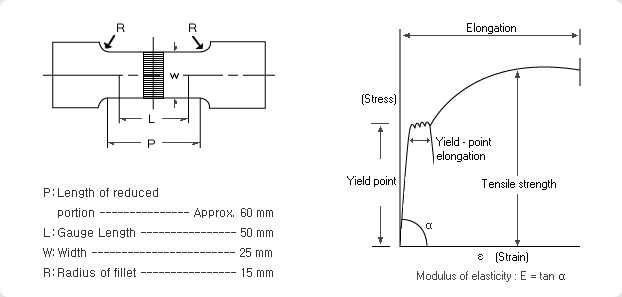
Tensile testing is performed to determine the yield strength, tensile strength, and elongation of steel sheet.
- Test Specimen / All types and sizes of test pieces for tension testing are prescribed in the Specifications of KS, JIS, and ASTM. Cold rolled steel sheet, for example, generally uses the specimen collection method indicated in KS B0801. NO.5
- Results / Tension test results are used as a basis for determining the workability and formability of steel sheet.
- Elongation / Greater elongation provides increased workability.
- Yield Point / A lower yield point gives better shape to the end product.
- Yield Ratio (yield point/tensile strength) / A lower yield ratio indicates widened differentiation between tensile strength and yield point. Greater difference translates into better workability.
- Modulus of Elasticity / The modulus of elasticity is in an inverse relationship with resistance to elastic strain. Lowered resistance indicates a better formed product.
- n-Value (Modulus of Work Hardening) / This measure is yielded when the stress- strain curve approximates ∂=CE". Workability is proportionate to the n-value.
- r-Value (Modulus of Plastic Deformation) / Surface shrinkage in the direction of thickness has an inverse relationship with the r-value and the shrinkage in the direction of width is directly proportionate to the r-value. The higher the value, the less susceptible to fracture, hence better drawability.
Bending Test
The bending test is performed to determine the ductility of steel sheet. The test specimen for cold-rolled steel sheet is designated in KS B 0801 No.3. In the test, the specimen is bent to a specified angle on a mandrel or a specified radius until fracture. The ductility of the sheet is judged by the cracks on the outside of the bent specimen. A cold-rolled sheet specimen is bent 180 degrees.

Hardness Test
Hardness of steel sheet is closely related to other properties like strength, wear resistance, and workability. The hardness test is an easy and effective method of identifying various properties of steel sheet. The Rockwell Hardness test is used for measuring the hardness of cold-rolled steel sheet. The test method is described as follows.
Rockwell Hardness Test
Material resistance to indentation is a qualitative indication of its strength. A steel ball or diamond is often used as an indenter. The hardness value is determined by the difference in penetration depth from the application of an initial minor load onto the indenter followed by a major load. The process is repeated twice. The penetration depth on the surface depends on the increase level in pure load, namely, the B-scale and the F-scale. The B-scale uses a 1/16 (1.588 mm) steel ball indenter and the major load is 100kg. The B-scale most accurately measures specimens with the thickness of 0.762mm (0.030 in.) or over. It is preferable to use the F-scale for specimens with a thickness under 0.762mm.
Workability Test
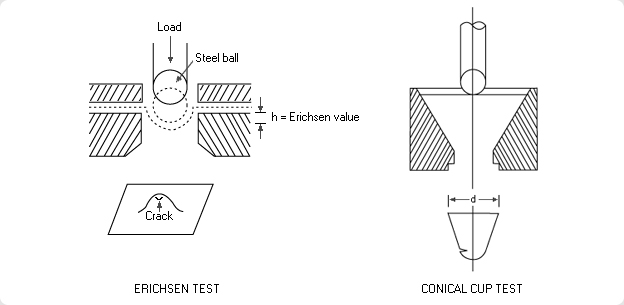
Tensile strength of cold-rolled steel sheet can be measured in various ways. Since tensile strength is developed through a complicated production process, it is difficult to measure the strength. The two most common ways to measure strength are:
- Erichsen Test - This test measures the drawability of steel sheet. As is shown in the diagram, a test specimen is punched down with a steel ball plunger until the test piece cracks. The h- value, measured when the fracture occurs, is the Erichsen value
- Conical Cup Test - This method has gained popularity in recent years. The specimen is pressed with a flat or round puncher as shown in the diagram. The test value is obtained by measuring the diameter of the cup that the specimen has been drawn into. Because the value closely corresponds to the actual performance of steel sheet fabrication, this test method is widely used by automobile makers.
Measurement Range

Note:
1. Sizes indicated in ![]() will be subjected to negotiation.
will be subjected to negotiation.
2. Coil is available with an inside diameter of 508㎜(20in.) or 610㎜(24in.)
3. Coil is available in weight ranging between 2.5 tons (5,500 lbs.) are 20 tons (44,000 lbs.)
Comparison of Standards
Chemical Components
|
Standard Specification |
Applications |
Chemical Component | |||||
|
C |
Si |
Mn |
P |
S | |||
| KS D 3512 (JIS G 3141) |
SPCC | CQ | ≤ 0.12 | - | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.040 | ≤ 0.045 |
| SPCD | DQ | ≤ 0.10 | - | ≤ 0.45 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 | |
| SPCE (N) | DDQ (Non-Aging) | ≤ 0.08 | - | ≤ 0.40 | ≤ 0.030 | ≤ 0.030 | |
| ASTM A 1008 | CS | CQ | ≤ 0.10 | - | ≤ 0.60 | ≤ 0.030 | ≤ 0.035 |
| DS | DQ | ≤ 0.08 | - | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.020 | ≤ 0.030 | |
| DDS | DDQ (Non-Aging) | ≤ 0.06 | - | ≤ 0.50 | ≤ 0.020 | ≤ 0.025 | |
| EN 10130 | DC01 (Fe P01) | CQ | ≤ 0.12 | - | ≤ 0.60 | ≤ 0.045 | ≤ 0.045 |
| DC03 (Fe P03) | DQ | ≤ 0.10 | - | ≤ 0.45 | ≤ 0.035 | ≤ 0.035 | |
| DC04 (Fe P04) | DDQ (Non-Aging) | ≤ 0.08 | - | ≤ 0.40 | ≤ 0.030 | ≤ 0.030 | |
| DC05 (Fe P05) | EDDQ | ≤ 0.06 | - | ≤ 0.35 | ≤ 0.025 | ≤ 0.025 | |
Mechanical Properties
|
Standard Specification |
Application |
Mechanical Property | ||||||||
|
Y.P |
T.S |
Elongation Min (%) | ||||||||
| Yielding Point (N/㎟) | Tensile Strength (N/㎟) |
0.25≤t <0.40 |
0.40≤t <0.60 |
0.60≤t <1.0 |
1.0≤t <1.6 |
1.6≤t <2.5 |
t≥2.5 | |||
| KS D 3512 (JIS G 3141) |
SPCC | CQ | - | ≥270 | (32) | (34) | (36) | (37) | (38) | (39) |
| SPCD | DQ | - | ≥270 | 34 | 36 | 38 | 39 | 40 | 41 | |
| SPCE (N) | DDQ (Non-Aging) | - | ≥270 | 36 | 38 | 40 | 41 | 42 | 43 | |
| ASTM A 1008 | CS | CQ | (140~275) | - | 30 (L0 =50mm) | |||||
| DS | DQ | (150~240) | - | 36 (L0 =50mm) | ||||||
| DDS | DDQ (Non-Aging) | (115~200) | - | 38 (L0 =50mm) | ||||||
| EDDS | EDDQ | (105~170) | - | 40 (L0 =50mm) | ||||||
| EN 10130 | DC01 (Fe P01) | CQ | ≤ 280 | 270~410 | 28 (L0 =80mm) | |||||
| DC03 (Fe P03) | DQ | ≤ 240 | 270~410 | 34 (L0 =80mm) | ||||||
| DC04 (Fe P04) | DDQ (Non-Aging) | ≤ 210 | 270~410 | 38 (L0 =80mm) | ||||||
| DC05 (Fe P05) | EDDQ | ≤ 180 | 270~410 | 40 (L0 =80mm) | ||||||
|
Standard Specification |
Mechanical Property | ||
|
Hardness | |||
|
Temper |
HRB |
Hv | |
| KS D 3512 (JIS G 3141) |
1/8H | 50~71 | 95~130 |
| 1/4H | 65~80 | 115~150 | |
| 1/2H | 74~89 | 135~185 | |
|
H |
≥85 | ≥170 | |
Standard Packing
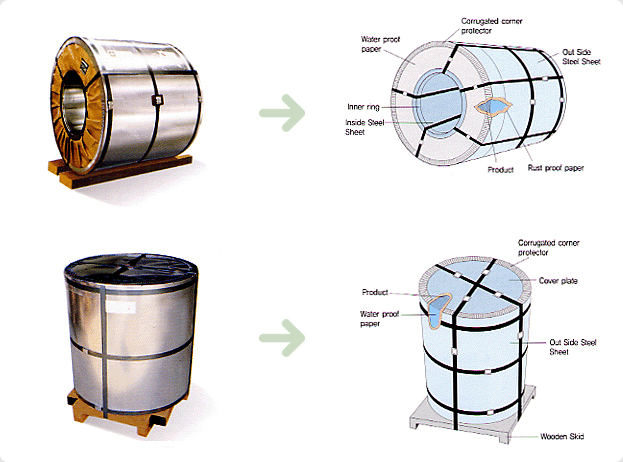
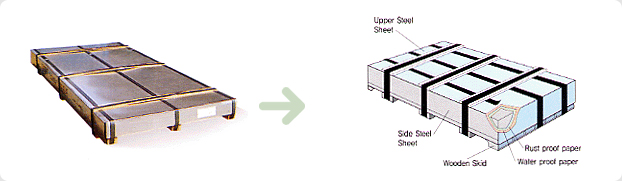
Dongbu Steel’s cold-rolled sheet and coil is packed to withstand handling during transportation and long-distance shipping. Special care is taken to prevent abrasion, rusting and scratching. Our packing procedure is illustrated below. The unit weight per package is usually between 2 and 5 tons for sheet and between 4 and 20 tons for coil.
Coil Packing
Sheet Packing
Sheet Weight Table
|
Weight |
Weight per Sheet | ||||||||||
|
Classification | |||||||||||
|
Thickness |
Width |
3ft (914mm) | 3.28ft (1,000mm) | 4ft (1,219mm) | 5ft (1,524mm) | ||||||
|
Length |
6ft (1,829mm) | 6,56ft (2,000mm) | 8ft (2,438mm) | 10ft (3,048mm) | |||||||
|
Weight Unit | |||||||||||
| in. | mm | lb/ft² | kg/㎡ | lb | kg | lb | kg | lb | kg | lb | kg |
| * 0.0079 | 0.20 | 0.3226 | 1.570 | 5.81 | 2.63 | 6.94 | 3.14 | 10.3 | 4.67 | 16.1 | 7.29 |
| 0.0091 | 0.23 | 0.3716 | 1.806 | 6.69 | 3.02 | 8.00 | 3.61 | 11.9 | 5.37 | 18.6 | 8.39 |
| * 0.0098 | 0.25 | 0.4002 | 1.962 | 7.20 | 3.28 | 8.61 | 3.92 | 12.8 | 5.83 | 20.0 | 9.11 |
| * 0.0106 | 0.27 | 0.4329 | 2.120 | 7.79 | 3.54 | 9.31 | 4.24 | 13.9 | 6.30 | 21.6 | 9.85 |
| * 0.0118 | 0.30 | 0.4819 | 2.355 | 8.67 | 3.94 | 10.4 | 4.71 | 15.4 | 7.00 | 24.1 | 10.9 |
| 0.0130 | 0.33 | 0.5309 | 2.590 | 9.56 | 4.33 | 11.4 | 5.18 | 17.0 | 7.70 | 26.5 | 12.0 |
| * 0.0138 | 0.35 | 0.5636 | 2.748 | 10.1 | 4.59 | 12.1 | 5.50 | 18.0 | 8.17 | 28.2 | 12.8 |
| * 0.0157 | 0.40 | 0.6412 | 3.140 | 11.5 | 5.25 | 13.8 | 6.28 | 20.5 | 9.33 | 32.1 | 14.6 |
| * 0.0177 | 0.45 | 0.7229 | 3.532 | 12.0 | 5.91 | 15.6 | 7.06 | 23.1 | 10.5 | 36.1 | 16.4 |
| * 0.0197 | 0.50 | 0.8045 | 3.925 | 14.5 | 6.56 | 17.3 | 7.85 | 25.7 | 11.7 | 40.2 | 18.2 |
| * 0.0217 | 0.55 | 0.8862 | 4.318 | 16.0 | 7.22 | 19.1 | 8.64 | 28.4 | 12.8 | 44.3 | 20.1 |
| * 0.0236 | 0.60 | 0.9638 | 4.710 | 17.3 | 7.88 | 20.7 | 9.42 | 30.8 | 14.0 | 48.2 | 21.9 |
| * 0.0276 | 0.70 | 1.127 | 5.495 | 20.3 | 9.19 | 24.2 | 11.0 | 36.1 | 16.3 | 56.4 | 25.5 |
| * 0.0315 | 0.80 | 1.287 | 6.280 | 23.2 | 10.5 | 27.7 | 12.6 | 41.2 | 18.7 | 64.4 | 29.2 |
| * 0.0354 | 0.90 | 1.446 | 7.065 | 26.0 | 11.8 | 31.1 | 14.1 | 46.3 | 21.0 | 72.3 | 32.8 |
| * 0.0394 | 1.00 | 1.609 | 7.850 | 29.0 | 13.1 | 34.6 | 15.7 | 51.5 | 23.3 | 80.5 | 36.5 |
| 0.0433 | 1.10 | 1.768 | 8.635 | 31.8 | 14.4 | 38.0 | 17.3 | 56.6 | 25.7 | 88.4 | 40.1 |
| * 0.0472 | 1.20 | 1.928 | 9.420 | 34.7 | 15.8 | 41.5 | 18.8 | 61.7 | 28.0 | 96.4 | 43.8 |
| 0.0512 | 1.30 | 2.091 | 10.20 | 37.6 | 17.1 | 45.0 | 20.4 | 66.9 | 30.3 | 105 | 47.4 |
| * 0.0551 | 1.40 | 2.250 | 10.99 | 40.5 | 18.4 | 48.4 | 22.0 | 72.0 | 32.7 | 113 | 51.0 |
| * 0.0591 | 1.50 | 2.414 | 11.78 | 43.5 | 19.7 | 51.9 | 23.6 | 77.2 | 35.0 | 121 | 54.7 |
| * 0.0630 | 1.60 | 2.573 | 12.56 | 46.3 | 21.0 | 55.4 | 25.1 | 82.3 | 37.3 | 129 | 58.3 |
| * 0.0709 | 1.80 | 2.896 | 14.13 | 52.1 | 23.6 | 62.3 | 28.3 | 92.7 | 42.0 | 145 | 65.6 |
| * 0.0787 | 2.00 | 3.214 | 15.70 | 57.9 | 26.3 | 69.2 | 31.4 | 103 | 46.7 | 161 | 72.9 |
| * 0.0906 | 2.30 | 3.700 | 18.06 | 66.6 | 30.2 | 79.6 | 36.1 | 118 | 53.7 | 185 | 83.9 |
| * 0.1024 | 2.60 | 4.182 | 20.41 | 75.3 | 34.1 | 90.0 | 40.8 | 134 | 60.7 | 209 | 94.8 |
| 0.1102 | 2.80 | 4.501 | 21.98 | 81.0 | 36.8 | 96.8 | 44.0 | 144 | 65.3 | 225 | 102 |
| * 0.1181 | 3.00 | 4.823 | 23.55 | 86.8 | 39.4 | 104 | 47.1 | 154 | 70.0 | 241 | 109 |
| * 0.1260 | 3.20 | 5.146 | 25.12 | 92.6 | 42.0 | 111 | 50.2 | 165 | 74.7 | 257 | 117 |
Note: These sizes are applicable to Korea industrial standards.
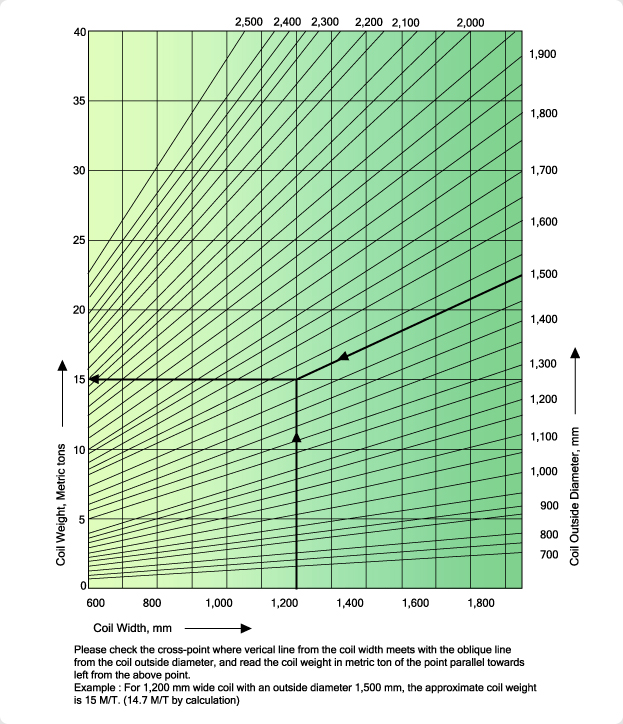
Width-Weight Curves for Coil
Inside Diameter is 508mm (20 in)
* Coil width is the same as that of the cold-rolled strip.
* The coil lamination factor is assumed to be 100%.
Hardness Test Comparison
| Rockwell Hardness | Vickers Hardness |
Rockwell Hardness | Vickers Hardness | ||||||
| B Scale | F Scale | Superficial | B Scale | F Scale | Superficial | ||||
| HB | HF | H30T | H15T | Hv | HB | HF | H30T | H15T | Hv |
| 100 | 113.3 | 80.8 | 90.6 | 235 | 75 | 99.3 | 64.8 | 82.8 | 140 |
| 99.5 | 113.0 | 80.5 | 232 | 74.5 | 99.0 | 64.4 | 138 | ||
| 99 | 112.7 | 80.1 | 90.3 | 229 | 74 | 98.7 | 64.1 | 82.5 | 137 |
| 98.5 | 112.4 | 79.8 | 227 | 73.5 | 98.5 | 63.8 | 136 | ||
| 98 | 112.1 | 7.5 | 90.0 | 224 | 73 | 98.2 | 63.5 | 82.2 | 134 |
| 97.5 | 111.9 | 79.2 | 221 | 72.5 | 97.9 | 63.2 | |||
| 97 | 111.6 | 78.9 | 89.7 | 218 | 72 | 97.6 | 62.8 | 81.9 | 132 |
| 96.5 | 111.3 | 78.5 | 216 | 71.5 | 97.3 | 62.5 | 131 | ||
| 96 | 111.0 | 78.2 | 89.4 | 214 | 71 | 97.1 | 62.2 | 81.6 | 129 |
| 95.5 | 110.7 | 77.9 | 211 | 70.5 | 96.8 | 61.9 | 128 | ||
| 95 | 110.5 | 77.6 | 89.1 | 209 | 70 | 96.5 | 61.6 | 81.3 | 127 |
| 94.5 | 110.2 | 77.3 | 207 | 69 | 95.9 | 60.9 | 81.0 | 125 | |
| 94 | 109.9 | 76.9 | 88.8 | 205 | 68 | 95.4 | 60.3 | 80.7 | 123 |
| 93.5 | 109.6 | 76.6 | 202 | 67 | 94.8 | 59.6 | 80.3 | 120 | |
| 93 | 109.3 | 76.3 | 88.5 | 200 | 66 | 94.3 | 59.0 | 80.0 | 119 |
| 92.5 | 109.1 | 76.0 | 198 | 65 | 93.7 | 58.4 | 79.7 | 117 | |
| 92 | 108.8 | 75.7 | 88.1 | 196 | 64 | 93.2 | 57.7 | 79.4 | 115 |
| 91.5 | 108.5 | 75.3 | 194 | 63 | 92.6 | 57.1 | 79.1 | 113 | |
| 91 | 108.2 | 75.0 | 87.8 | 192 | 62 | 92.0 | 56.4 | 78.8 | 111 |
| 90.5 | 107.9 | 74.7 | 190 | 61 | 91.5 | 55.8 | 78.5 | 109 | |
| 90 | 107.7 | 74.4 | 87.5 | 188 | 60 | 90.9 | 55.2 | 78.2 | 107 |
| 89.5 | 107.4 | 74.1 | 186 | 59 | 90.4 | 54.5 | 77.8 | 106 | |
| 89 | 107.1 | 73.7 | 87.2 | 184 | 58 | 89.8 | 53.9 | 77.5 | 104 |
| 88.5 | 106.8 | 73.4 | 182 | 57 | 89.2 | 53.2 | 77.2 | 103 | |
| 88 | 106.6 | 73.1 | 86.9 | 180 | 56 | 88.7 | 52.6 | 76.9 | 102 |
| 87.5 | 106.3 | 72.8 | 178 | 55 | 88.1 | 51.9 | 76.6 | 100 | |
| 87 | 106.0 | 72.4 | 86.6 | 176 | 54 | 87.5 | 51.3 | 76.3 | 99 |
| 86.5 | 105.7 | 72.1 | 175 | 53 | 87.0 | 50.7 | 75.9 | 98 | |
| 86 | 105.4 | 71.8 | 86.3 | 173 | 52 | 86.5 | 50.0 | 75.7 | 96 |
| 85.5 | 105.2 | 71.5 | 171 | 51 | 85.9 | 49.4 | 75.4 | 95 | |
| 85 | 104.9 | 71.2 | 86.0 | 170 | 50 | 85.3 | 48.7 | 75.0 | 94 |
| 84.5 | 104.6 | 70.8 | 168 | 49 | 84.8 | 48.1 | 74.7 | 93 | |
| 84 | 104.3 | 70.5 | 85.6 | 166 | 48 | 84.2 | 47.5 | 74.4 | 92 |
| 83.5 | 104.0 | 70.2 | 164 | 47 | 83.7 | 46.8 | 74.1 | 91 | |
| 83 | 103.8 | 69.9 | 85.4 | 163 | 46 | 83.1 | 46.2 | 73.8 | 90 |
| 82.5 | 103.5 | 69.6 | 161 | 45 | 82.5 | 45.5 | 73.5 | 89 | |
| 82 | 103.2 | 69.2 | 85.0 | 160 | 44 | 82.0 | 44.9 | 73.2 | 88 |
| 81.5 | 102.9 | 68.9 | 158 | 43 | 81.4 | 44.3 | 72.9 | 87 | |
| 81 | 102.6 | 68.6 | 84.7 | 156 | 42 | 80.9 | 43.6 | 72.5 | 86 |
| 80.5 | 102.4 | 68.3 | 155 | 41 | 80.3 | 43.0 | 72.2 | 85 | |
| 80 | 102.1 | 68.0 | 84.4 | 154 | 40 | 79.3 | 42.3 | 71.9 | 84 |
| 79.5 | 101.8 | 67.6 | 152 | 39 | 79.2 | 41.7 | 71.6 | 83 | |
| 79 | 101.5 | 67.3 | 84.1 | 150 | 38 | 78.6 | 41.1 | 71.3 | 82 |
| 78.5 | 101.2 | 67.0 | 149 | 37 | 78.1 | 40.4 | 71.0 | 81 | |
| 78 | 101.0 | 66.7 | 83.7 | 147 | 36 | 77.5 | 39.8 | 70.7 | 80 |
| 77.5 | 100.7 | 66.4 | 146 | 35 | 77.0 | 39.1 | 70.4 | 80 | |
| 77 | 100.4 | 66.0 | 83.5 | 145 | 34 | 76.4 | 38.5 | 70 | 80 |
| 76.5 | 100.1 | 65.7 | 144 | 33 | 75.8 | 37.9 | 69.7 | 78 | |
| 76 | 99.9 | 65.4 | 83.2 | 142 | 32 | 75.3 | 37.2 | 69.4 | 78 |
| 75.5 | 99.6 | 65.1 | 141 | 31 | 74.7 | 36.6 | 68.1 | 77 | |
Comparison of Gauges
| Gauge No. |
U.S.G. | B.W.G. | B.G. | S.W.G. | M.S.G. | G.S.G. | ||||||
| mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | mm | in. | |
| 10 | 3.572 | 0.1406 | 3.40 | 0.134 | 3.175 | 0.1250 | 3.251 | 0.128 | 3.416 | 0.1345 | 3.510 | 0.1382 |
| 11 | 3.175 | 0.1250 | 3.05 | 0.120 | 2.827 | 0.1113 | 2.946 | 0.116 | 3.037 | 0.1196 | 3.132 | 0.1233 |
| 12 | 2.778 | 0.1094 | 2.77 | 0.109 | 2.517 | 0.0991 | 2.64 | 0.104 | 2.657 | 0.1046 | 2.753 | 0.1084 |
| 13 | 2.381 | 0.0938 | 2.41 | 0.095 | 2.240 | 0.0882 | 2.34 | 0.092 | 2.278 | 0.0897 | 2.372 | 0.0934 |
| 14 | 1.984 | 0.0781 | 2.11 | 0.083 | 1.994 | 0.0785 | 2.03 | 0.080 | 1.897 | 0.0747 | 1.994 | 0.0785 |
| 15 | 1.786 | 0.0703 | 1.83 | 0.072 | 1.775 | 0.0699 | 1.83 | 0.072 | 1.709 | 0.0673 | 1.803 | 0.0710 |
| 16 | 1.588 | 0.0625 | 1.65 | 0.065 | 1.588 | 0.0625 | 1.63 | 0.064 | 1.519 | 0.0598 | 1.613 | 0.0635 |
| 17 | 1.429 | 0.0563 | 1.47 | 0.058 | 1.412 | 0.0556 | 1.42 | 0.056 | 1.367 | 0.0538 | 1.461 | 0.0575 |
| 18 | 1.2700 | 0.0500 | 1.24 | 0.049 | 1.257 | 0.0495 | 1.22 | 0.048 | 1.214 | 0.0478 | 1.311 | 0.0516 |
| 19 | 1.1113 | 0.0438 | 1.07 | 0.042 | 1.118 | 0.0440 | 1.02 | 0.040 | 1.062 | 0.0418 | 1.158 | 0.0456 |
| 20 | 0.9525 | 0.0375 | 0.89 | 0.035 | 0.996 | 0.0392 | 0.91 | 0.036 | 0.912 | 0.0359 | 1.006 | 0.0396 |
| 21 | 0.8731 | 0.0344 | 0.81 | 0.032 | 0.886 | 0.0349 | 0.81 | 0.032 | 0.836 | 0.0329 | 0.930 | 0.0366 |
| 22 | 0.7938 | 0.0313 | 0.71 | 0.028 | 0.794 | 0.0313 | 0.71 | 0.028 | 0.760 | 0.0299 | 0.853 | 0.0336 |
| 23 | 0.7144 | 0.0281 | 0.64 | 0.025 | 0.707 | 0.0278 | 0.61 | 0.024 | 0.683 | 0.0269 | 0.777 | 0.0306 |
| 24 | 0.6350 | 0.0250 | 0.56 | 0.022 | 0.629 | 0.0248 | 0.56 | 0.022 | 0.607 | 0.0239 | 0.701 | 0.0276 |
| 25 | 0.5556 | 0.0219 | 0.51 | 0.020 | 0.560 | 0.0220 | 0.51 | 0.020 | 0.531 | 0.0209 | 0.627 | 0.0247 |
| 26 | 0.4763 | 0.0188 | 0.46 | 0.018 | 0.498 | 0.0196 | 0.46 | 0.018 | 0.455 | 0.0179 | 0.551 | 0.0217 |
| 27 | 0.4366 | 0.0172 | 0.41 | 0.016 | 0.443 | 0.0175 | 0.417 | 0.0164 | 0.417 | 0.0164 | 0.513 | 0.0202 |
| 28 | 0.3969 | 0.0156 | 0.36 | 0.014 | 0.397 | 0.0156 | 0.376 | 0.0148 | 0.378 | 0.0149 | 0.475 | 0.0187 |
| 29 | 0.3572 | 0.0141 | 0.33 | 0.013 | 0.353 | 0.0139 | 0.345 | 0.0136 | 0.343 | 0.0135 | 0.437 | 0.0172 |
| 30 | 0.3175 | 0.0125 | 0.30 | 0.012 | 0.312 | 0.0123 | 0.315 | 0.0124 | 0.305 | 0.0120 | 0.399 | 0.0157 |
| 31 | 0.2778 | 0.0109 | 0.25 | 0.011 | 0.279 | 0.0110 | 0.295 | 0.0116 | 0.267 | 0.0105 | 0.361 | 0.0142 |
| 32 | 0.2580 | 0.0102 | 0.23 | 0.009 | 0.249 | 0.0098 | 0.274 | 0.0108 | 0.246 | 0.0097 | 0.340 | 0.0134 |
| 33 | 0.2381 | 0.0094 | 0.20 | 0.008 | 0.221 | 0.0087 | 0.254 | 0.0100 | 0.229 | 0.0090 | - | - |
| 34 | 0.2183 | 0.0086 | 0.18 | 0.007 | 0.196 | 0.0077 | 0.234 | 0.0092 | 0.208 | 0.0082 | - | - |
| 35 | 0.1984 | 0.0078 | 0.13 | 0.005 | 0.175 | 0.0069 | 0.213 | 0.0084 | 0.191 | 0.0075 | - | - |
Note
| U.S.G = United States Standard Gauge Wrough Iron 401b/f²-in. B.W.G = Birmingham Wire Gauge B.G = Birmingham Gauge |
S.W.G = Standard Wire Gauge M.S.G = Manufacturer's Standard Gauge 40321b/f²-in. G.S.G = Galvanized Sheet Gauge |
Conversion Factors
Weight
| Classification | Kilogram | Ounce | Pound | Short Ton (2,000 lbs) |
Long Ton (2,240 lbs) |
Metric Ton (1,000 kg) |
| kg | oz | lb | st | lt | t | |
| Kilogram (kg) | 1 | 35.2740 | 2.20462 | 0.001102 | 0.0₃9842 | 0.001 |
| Ounce (oz) | 0.02835 | 1 | 0.06250 | 0.0₄3125 | 0.0₄2790 | 0.0₄2835 |
| Pound (lb) | 0.45359 | 16 | 1 | 0.00050 | 0.0₃4464 | 0.0₃4536 |
| Short Ton (st) | 907.185 | 32,000 | 2,000 | 1 | 0.89286 | 0.90719 |
| Long Ton (lt) | 1,016.05 | 35,840 | 2,240 | 1.12 | 1 | 1.01605 |
| Metric Ton (t) | 1,000 | 35,274 | 2,204.62 | 1.10231 | 0.98421 | 1 |
(Example 0.0₃9842 = 0.0009842)
Linear Measure
| Classification | Millimeter | Centimeter | Meter | Inch | Foot | Yard | Mile |
| kg | oz | lb | st | lt | t | mi | |
| Millimeter(mm) | 1 | 0.1 | 0.001 | 0.03937 | 0.0032808 | 0.0010936 | 0.06214 |
| Centimeter(cm) | 10 | 1 | 0.01 | 0.3937 | 0.032808 | 0.010936 | 0.06214 |
| Meter(m) | 1,000 | 100 | 1 | 39.37 | 3.28083 | 1.0936 | 0.06214 |
| Inch(in.) | 25.40 | 2.540 | 0.0254 | 1 | 0.0833 | 0.02778 | 0.01578 |
| Foot(ft) | 304.8 | 30.48 | 0.3048 | 12 | 1 | 0.3333 | 0.01894 |
| Yard(yd) | 914.4 | 91.44 | 0.9144 | 36 | 3 | 1 | 0.05682 |
| Mile(mi) | 1,609,347.0 | 160,934,.70 | 1,609.35 | 63,360 | 5,280 | 1,760 | 1 |




 |
| 


